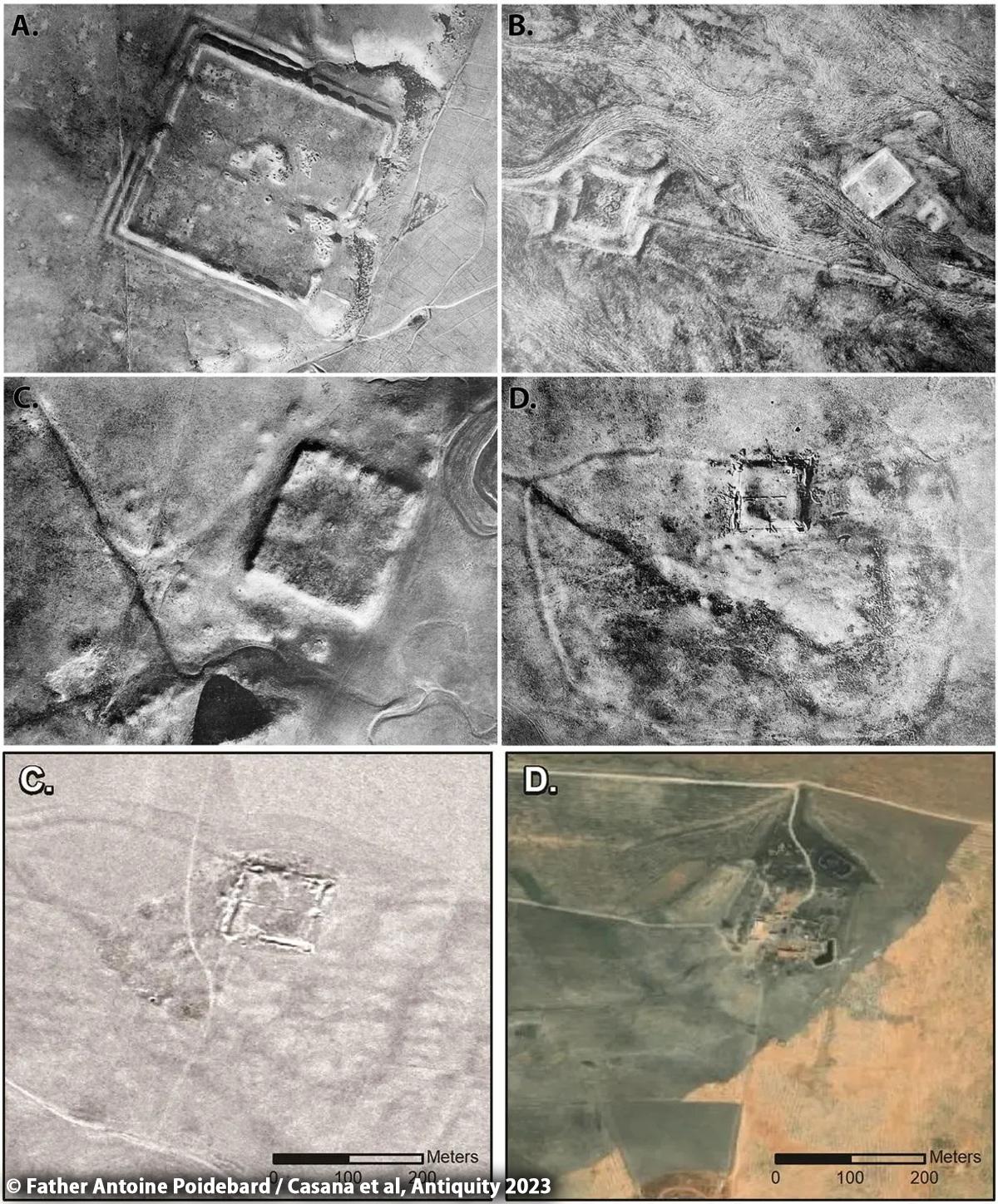
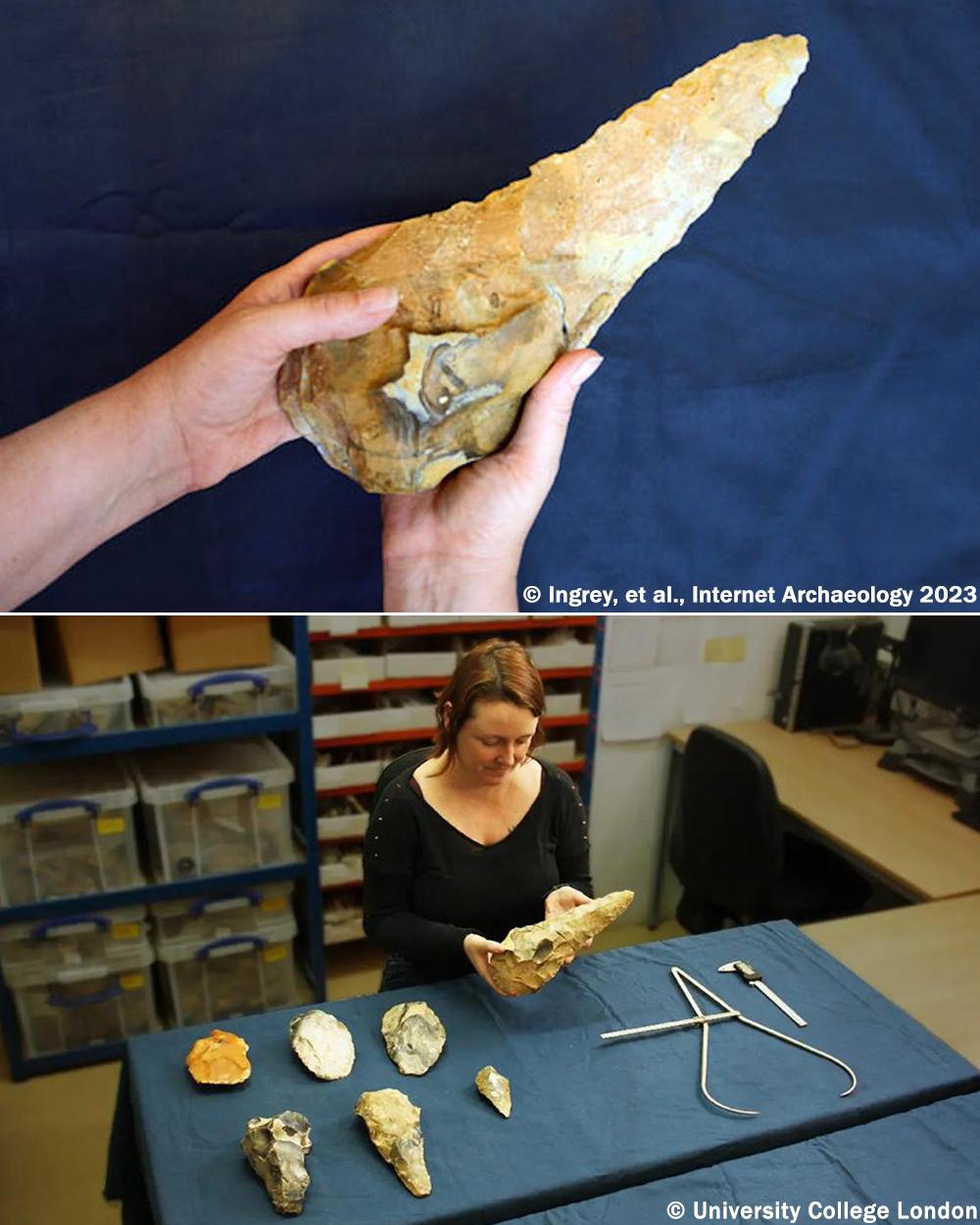
Mesopotamia, often referred to as the cradle of civilization in the West, holds a profound significance in the annals of human history.
Exploring the Cradle of Civilization in Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia, often referred to as the cradle of civilization in the West, holds a profound significance in the annals of human history. Dating back to at least 6,000 BC, this ancient region nestled between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers witnessed the birth of some of the earliest known civilizations, including the Sumerians, Akkadians, Babylonians, and Assyrians. In this blog post, we delve into the rich tapestry of Mesopotamian history, exploring its cultural achievements, technological innovations, and enduring legacy that continues to shape the modern world.

The Rise of Civilization in Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia's fertile soil and strategic location between the great rivers provided an ideal environment for human settlement and agricultural development. The ancient Mesopotamians, adept at harnessing the power of irrigation, cultivated crops such as barley, wheat, and dates, laying the foundation for sedentary life and urbanization. As populations grew, city-states emerged, each governed by its own ruler and administrative system. This period witnessed the rise of monumental architecture, including ziggurats, temples, and palaces, showcasing the ingenuity and ambition of Mesopotamian civilization.
Cultural and Technological Advancements
Mesopotamia was a melting pot of diverse cultures and ethnicities, fostering intellectual exchange and cultural innovation. The region gave birth to the world's first writing system, cuneiform, which enabled the recording of laws, literature, and administrative records on clay tablets. Additionally, Mesopotamians made significant strides in mathematics, astronomy, and medicine, developing concepts such as the sixty-minute hour, the twelve-month calendar, and the principles of surgical techniques. These advancements laid the groundwork for future scientific inquiry and shaped the intellectual landscape of the ancient world.
The Legacy of Mesopotamian Civilization
The legacy of Mesopotamia extends far beyond its ancient borders, permeating virtually every aspect of modern society. Many aspects of daily life, including writing, agriculture, and governance, trace their origins back to Mesopotamian innovations. The epic of Gilgamesh, one of the earliest known literary works, continues to captivate readers with its timeless themes of heroism, friendship, and the quest for immortality. Moreover, Mesopotamian religious beliefs and mythologies, embodied in deities such as Enlil, Inanna, and Marduk, have left an indelible mark on subsequent religious traditions, influencing the development of Judaism, Christianity, and Islam.
Exploring Ancient Discoveries in Mesopotamia
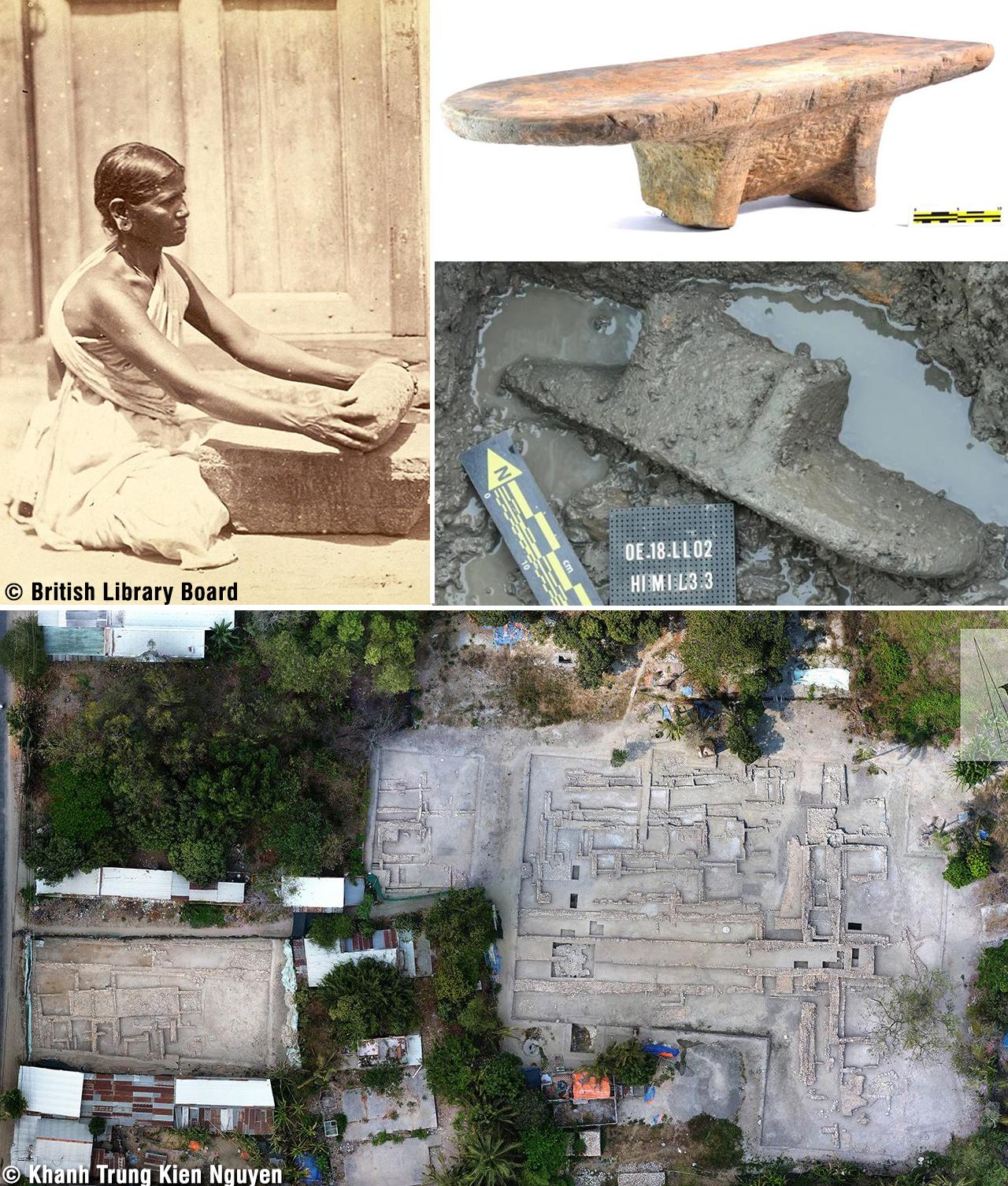
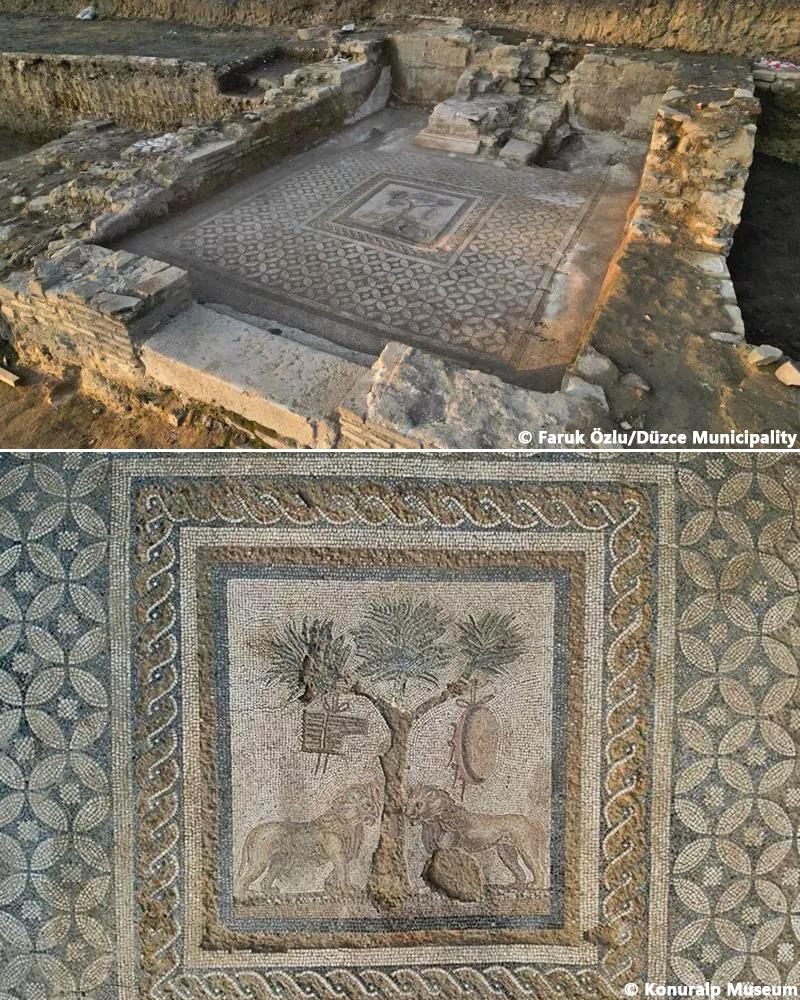
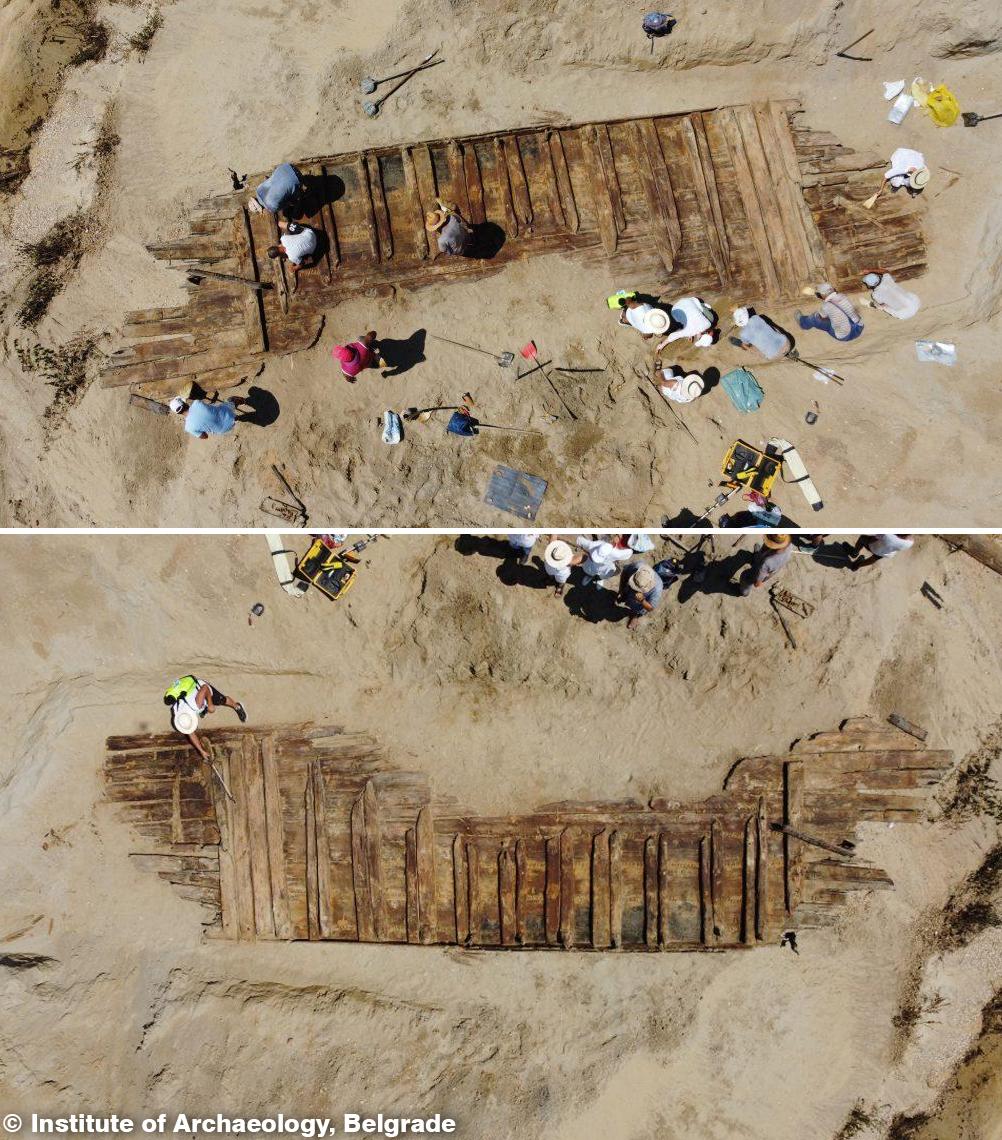
The archaeological treasures of Mesopotamia offer a window into the rich tapestry of its past, allowing us to glimpse the achievements and aspirations of its ancient inhabitants. From the majestic ruins of Babylon and Nineveh to the intricate artifacts housed in museums around the world, each discovery sheds light on different facets of Mesopotamian life and culture. Recent excavations have uncovered new insights into the daily lives of ancient Mesopotamians, revealing their social structures, economic activities, and religious practices in greater detail than ever before.
In conclusion, Mesopotamia stands as a testament to the ingenuity, creativity, and resilience of humanity. From its humble beginnings as a collection of riverine settlements to its zenith as a cradle of civilization, Mesopotamia has left an indelible imprint on the course of human history. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of this ancient land, we gain a deeper appreciation for the enduring legacy of Mesopotamian civilization and its profound impact on the world we inhabit today.